- Enhanced orchestration and hugepages
- VyOS install
- Basic VyOS setup
- VyOS Setup and perfomance test(Virtio)
- VyOS Setup and perfomance test(SR-IOV)
In first part I did a general overview of the functionality and principles of operation of the NFX250, and also made JCP performance test.
Now its time to use NFX for its intended purpose and launch the virtual router.
From the available open source projects that can be used as a router, I have chosed to install VyOS on NFX250. You can also try FRR.
Enhanced-orchestration and hugepages
Junos V2 architecture is used, software version 18.4R3.
To deploy virtual machines from JDM, you need to enable enhanced-orchestration and hugepages functionality. You will have to remove all interfaces and reload JDM.
You will need console access.
My NFX250-ATT-LS1 has only 16Gb of memory. For the correct operation of JCP, JDM and the hypervisor, 6-8 Gb of memory is required. This means that we can allocate 8Gb for user virtual machines.
{master:0}[edit]
root@jdm# set system services enhanced-orchestration
root@jdm# set system memory hugepages page-size 1024 page-count 8
## Warning: bridges stanza not allowed if system services enhanced-orchestration is configured
## Warning: interface stanza not allowed if system services enhanced-orchestration is configured
## Warning: route stanza not allowed if system services enhanced-orchestration is configured
root@jdm# delete interface eth0br
root@jdm# delete route
root@jdm# delete interface jmgmt0
root@jdm# delete apply-groups 1604-config
root@jdm# delete groups 1604-config
{master:0}[edit]
root@jdm# commit and-quit
commit complete
root@jdm> request system reboot
Reboot the system ? [yes,no] (no) yes
System reboot operation started, please wait...
After rebooting, I set up the management again:
{master:0}[edit]
root@jdm# set interfaces jmgmt0 unit 0 family inet dhcp
root@jdm# commit
commit complete
VyOS install
After enabling enhanced-orchestration, the VNF configuration functionality from the JDM becomes available. In fact, it’s just Junos wrapper for creating VMs XML config files. The VyOS Rolling version is available for free download on the official website.
{master:0}
root@jdm> start shell
jdm:~#cd /var/third-party
jdm:/var/third-party# wget https://downloads.vyos.io/rolling/current/amd64/vyos-rolling-latest.iso
Creating HDD disk for installing VyOS:
jdm:/var/third-party# qemu-img create -f qcow2 vyos.qcow2 2G
Formatting 'vyos.qcow2', fmt=qcow2 size=2147483648 encryption=off cluster_size=65536 lazy_refcounts=off
Config for VyOS VNF:
[edit]
virtual-network-functions vyos {
image {
/var/third-party/vyos.qcow2;
image-type qcow2;
bus-type virtio;
}
virtual-cpu {
count 6;
features {
hardware-virtualization;
}
}
no-default-interfaces;
interfaces eth0 {
management internal;
}
memory {
size 4096000;
features {
hugepages {
page-size 1024;
}
}
}
storage sdb {
type {
cdrom {
source {
file /var/third-party/images/vyos-rolling-latest.iso;
}
}
}
}
}
In Junos 18.4R3.3, I did not find functionality to set cd-rom as a boot disk. I have added a line with the option to boot from cd-rom using virsh:
jdm:~#virsh edit vyos
<os>
<type arch='x86_64' machine='pc-i440fx-1.7'>hvm</type>
+ <boot dev='cdrom'/>
<boot dev='hd'/>
<smbios mode='sysinfo'/>
</os>
Restart the virtual machine to boot from the iso image:
jdm:~# virsh destroy vyos
Domain vyos destroyed
jdm:~# virsh start vyos
Domain vyos started
To install VyOS, i will connect to VM with the virsh console. After installation, i will need to turn off the virtual machine and revert back boot options:
jdm:~# virsh console vyos
#boot sequence omitted
vyos login: vyos
Password:
Linux vyos 5.10.14-amd64-vyos #1 SMP Tue Feb 16 09:38:59 UTC 2021 x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
vyos@vyos:~$ install image
Welcome to the VyOS install program. This script
will walk you through the process of installing the
VyOS image to a local hard drive.
Would you like to continue? (Yes/No) [Yes]:
Probing drives: OK
Looking for pre-existing RAID groups...none found.
The VyOS image will require a minimum 2000MB root.
Would you like me to try to partition a drive automatically
or would you rather partition it manually with parted? If
you have already setup your partitions, you may skip this step
Partition (Auto/Parted/Skip) [Auto]:
I found the following drives on your system:
vda 2147MB
Install the image on? [vda]:
This will destroy all data on /dev/vda.
Continue? (Yes/No) [No]: yes
How big of a root partition should I create? (2000MB - 2147MB) [2147]MB:
Creating filesystem on /dev/vda1: OK
Done!
Mounting /dev/vda1...
What would you like to name this image? [1.4-rolling-202102162107]:
OK. This image will be named: 1.4-rolling-202102162107
Copying squashfs image...
Copying kernel and initrd images...
Done!
I found the following configuration files:
/opt/vyatta/etc/config/config.boot
/opt/vyatta/etc/config.boot.default
Which one should I copy to vda? [/opt/vyatta/etc/config/config.boot]:
Copying /opt/vyatta/etc/config/config.boot to vda.
Enter password for administrator account
Enter password for user 'vyos':
Retype password for user 'vyos':
I need to install the GRUB boot loader.
I found the following drives on your system:
vda 2147MB
Which drive should GRUB modify the boot partition on? [vda]:
Setting up grub: OK
Done!
vyos@vyos:~$ poweroff
Are you sure you want to poweroff this system? [y/N] y
[ 298.141695] systemd-shutdown[1]: Failed to parse (null): No such file or directory
[ 298.142995] systemd-shutdown[1]: Failed to deactivate swaps: No such file or directory
[ 298.148160] [1960]: Failed to unmount /usr/lib/live/mount/medium: Device or resource busy
[ 298.208396] reboot: Power down
error: One or more references were leaked after disconnect from the hypervisor
Reverting back boot order and start VyOS:
jdm:~#virsh edit vyos
<os>
<type arch='x86_64' machine='pc-i440fx-1.7'>hvm</type>
- <boot dev='cdrom'/>
<boot dev='hd'/>
<smbios mode='sysinfo'/>
</os>
jdm:~#virsh start vyos
This completes the VyOS installation, let’s move on to configuring and testing.
Basic VyOS setup
I’ll start by setting up management.
When configuring VNF for VyOS, only one interface was allocated – management internal. It is responsible for the connectivity with JDM . For correct operation, you need to enable the DHCP client on this interface. Also, I will add an interface for management, which is connected to the out-of-band management bridge.
{master:0}
root@jdm> configure
root@jdm# set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth1 management out-of-band
root@jdm# commit and-quit
commit complete
root@jdm> request virtual-network-functions console vyos
Connected to domain vyos
Escape character is ^]
vyos login: vyos
Password:
Linux vyos 5.10.14-amd64-vyos #1 SMP Tue Feb 16 09:38:59 UTC 2021 x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
vyos@vyos# set interfaces ethernet eth0 address dhcp
vyos@vyos# set interfaces ethernet eth1 address dhcp
vyos@vyos# set service ssh
vyos@vyos# commit
Now you can use JDM to manage VyOS, as well as connect via SSH from the management network.
root@jdm> show virtual-network-functions
ID Name State Liveliness
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6 vyos Running alive
1 vjunos0 Running alive
10216 jdm Running alive
root@jdm> ssh vyos@vyos
Welcome to VyOS
vyos@vyos's password:
Linux vyos 5.10.14-amd64-vyos #1 SMP Tue Feb 16 09:38:59 UTC 2021 x86_64
vyos@vyos:~$
The virtual machine is available from the management network, now i need to set up communication with the outside world.
On the NFX250, this can be done in two ways:
-Virtio (service chaining using vlans)
-SR-IOV (Service Chaining with SR-IOV (Single Root Input / Output Virtualization)).
VyOS Setup and perfomance test(Virtio)
I’ll start testing with a variant that uses Vitrio interfaces.
Virtio is the easiest and fastest option for deploying services. However, in this case, the entire load falls on the hypervisor and depends mainly on the performance of the CPU.
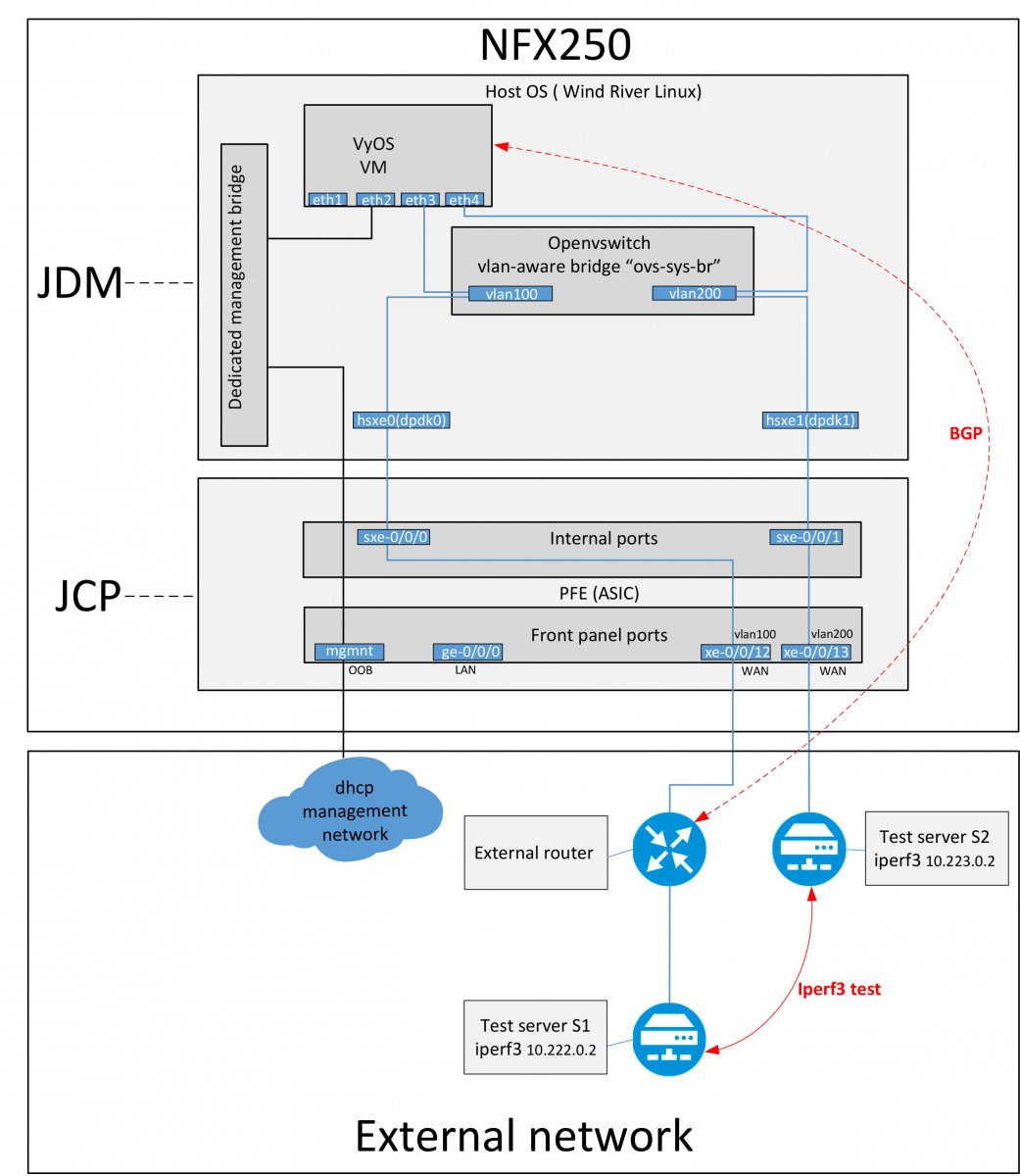
Lab diagram for testing VyOS and virtio:
To communicate with the outside world, you need to configure JCP:
{master:0}[edit]
root#set vlans vlan100 vlan-id 100
root#set vlans vlan200 vlan-id 200
root#set interfaces xe-0/0/12 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access
root#set interfaces xe-0/0/12 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan100
root#set interfaces xe-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode access
root#set interfaces xe-0/0/13 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan200
root#set interfaces sxe-0/0/0.0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
root#set interfaces sxe-0/0/0.0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan100
root#set interfaces sxe-0/0/1.0 family ethernet-switching interface-mode trunk
root#set interfaces sxe-0/0/1.0 family ethernet-switching vlan members vlan200
root# commit
commit complete
All configuration related to VM connectivity is done in JDM.
Will need to add interfaces for VyOS and create vlans on the hypervisor:
{master:0}[edit]
root@jdm#set host-os vlans vlan100 vlan-id 100
root@jdm#set host-os vlans vlan200 vlan-id 200
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth3 mapping vlan mode access
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth3 mapping vlan members vlan100
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth4 mapping vlan mode access
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth4 mapping vlan members vlan200
root@jdm# commit
commit complete
VyOS config:
interfaces {
ethernet eth0 {
address dhcp
description internal Management
hw-id b0:33:a6:33:f3:cf
}
ethernet eth1 {
address dhcp
description OOB Management
hw-id b0:33:a6:33:f3:d0
}
ethernet eth2 {
address 172.16.23.2/30
description BGP-to-ext-network
hw-id b0:33:a6:33:f3:d2
}
ethernet eth3 {
address 10.223.0.1/24
description S2-test-server
hw-id b0:33:a6:33:f3:d3
}
}
protocols {
bgp 65234 {
address-family {
ipv4-unicast {
network 10.223.0.0/24 {
}
}
}
neighbor 172.16.23.1 {
address-family {
ipv4-unicast {
route-map {
export export
}
}
}
remote-as 65230
}
}
}
iperf3 test on virtio interfaces:
[root@s2]# iperf3 -c 10.222.0.2 -p 5201
Connecting to host 10.222.0.2, port 5201
[ 4] local 10.223.0.2 port 58654 connected to 10.222.0.2 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 340 MBytes 2.85 Gbits/sec 57 331 KBytes
#######OMMITED############
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 3.53 GBytes 3.03 Gbits/sec 918 sender
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 3.53 GBytes 3.03 Gbits/sec receiver
iperf Done.
[root@s2]# iperf3 -c 10.222.0.2 -p 5201 -R
Connecting to host 10.222.0.2, port 5201
Reverse mode, remote host 10.222.0.2 is sending
[ 4] local 10.223.0.2 port 58662 connected to 10.222.0.2port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 330 MBytes 2.77 Gbits/sec
#######OMMITED############
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 2.98 GBytes 2.56 Gbits/sec 637 sender
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 2.98 GBytes 2.56 Gbits/sec receiver
Result on Virtio:
2.56Gbit / 3.03Gbit
Not bad.
Let’s try the same with SR-IOV.
VyOS Setup and perfomance test(SR-IOV)
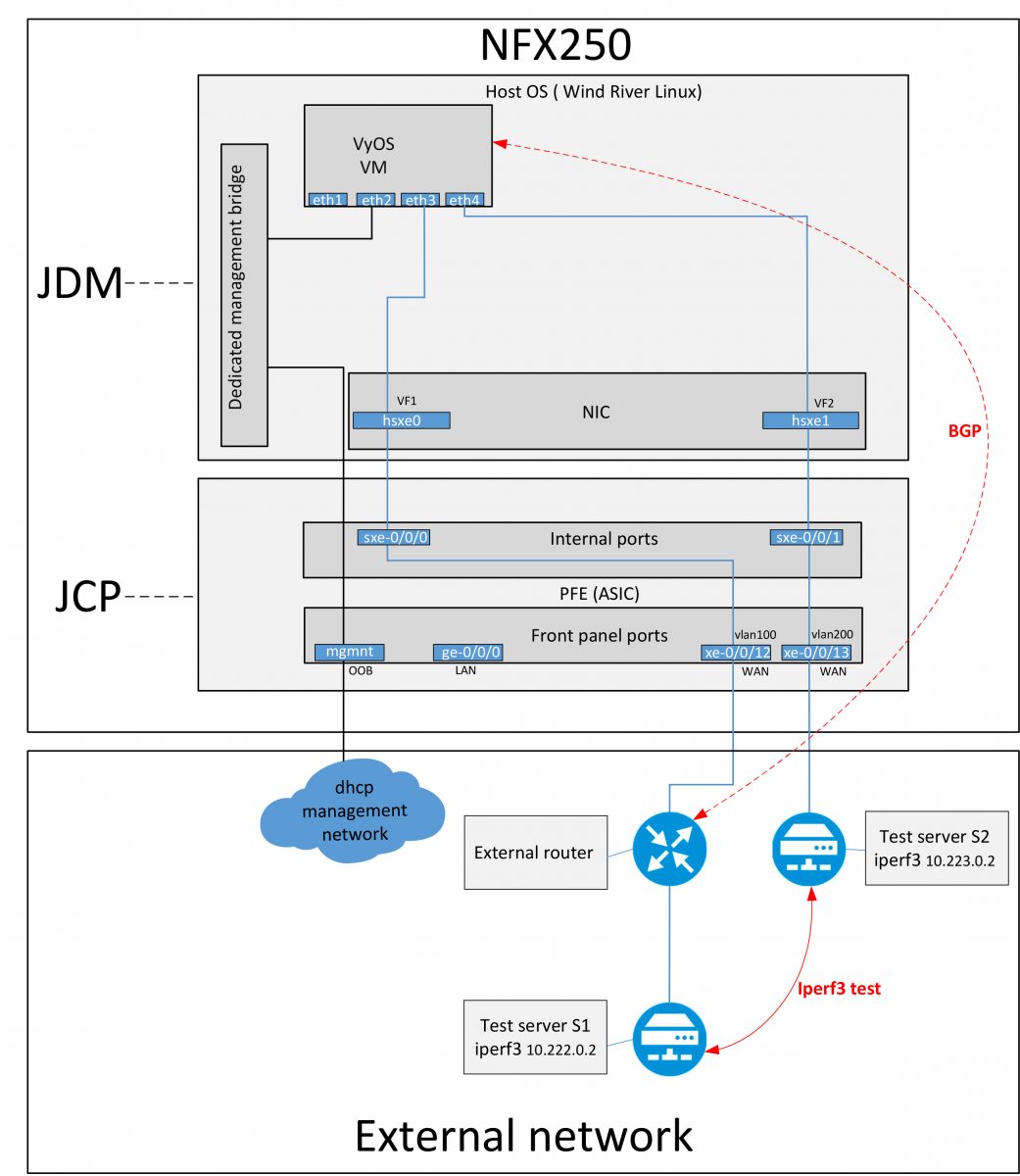
SR-IOV provides shared access to PCI-Experss resources. The physical interface is divided into a certain number of VFs (Virtual Functions), each of which can be connected to a virtual machine. Different amounts of VF are available depending on the equipment model.
SR-IOV is less CPU intensive and provides faster lower latency.
Lab diagram for testing VyOS and SR-IOV:
Changing the port configuration of the virtual machine to SR-IOV:
root@jdm#delete virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth3 mapping vlan
root@jdm#delete virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth4 mapping vlan
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth3 mapping hsxe0 virtual-function vlan-id 100
root@jdm#set virtual-network-functions vyos interfaces eth4 mapping hsxe1 virtual-function vlan-id 200
root@jdm# commit
commit complete
Iperf3 test on SR-IOV interfaces:
[root@s2]# iperf3 -c 10.222.0.2 -p 5201 -R
Connecting to host 10.222.0.2, port 5201
Reverse mode, remote host 10.222.0.2 is sending
[ 4] local 10.223.0.2 port 58626 connected to 10.222.0.2 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 458 MBytes 3.84 Gbits/sec
#######OMMITED############
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 4.53 GBytes 3.89 Gbits/sec 312 sender
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 4.53 GBytes 3.89 Gbits/sec receiver
iperf Done.
[root@s2]# iperf3 -c 10.222.0.2 -p 5201
Connecting to host 10.222.0.2, port 5201
[ 4] local 10.223.0.2 port 58630 connected to 10.222.0.2 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 513 MBytes 4.30 Gbits/sec 54 645 KBytes
#######OMMITED############
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 5.08 GBytes 4.37 Gbits/sec 186 sender
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 5.08 GBytes 4.37 Gbits/sec receiver
iperf Done.
Result on SR-IOV:
3.89Gbit / 4.37Gbit
Much better.
Let me remind you that the test is performed on the NFX250-ATT-LS1, which is the low end model in the NFX250 line. Based on the test results, i can say that Juniper has released an interesting product on the basis of which almost any service can be quickly deployed. I belive we can expect a significant increase in performance on top NFX250 models.